DR SACHIN VIJAY NAIKNAWARE. GYNAEC LAPAROSCOPIC SURGEON.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Endometriosis is defined as presence and proliferation of functional endometrial glands and storm outside uterine cavity. it is a multifactorial oestrogen dependent disease affecting 5-10% of women in reproductive age group. in women with dysmenorrhea its incidence is as high as 40-60% and endometriosis is seen in approximately 20-30% of women with sub-fertility.
It is commonly seen in age group of 25-35 years and supposed to be more common in thin taller women with low body mass index, delayed pregnancy or no pregnancy, early menarche late menopause,are some of the risk factors associated with endometriosis.
Before starting treatment of any condition it is better to look at what causes the above condition? what symptoms amongst all are severe and needs immediate attention? is there a permanent cure of the condition? what best symptomatic relief is there with medicine or surgical intervention? and how to best relieve the symptoms? to address all the above question we will look shortly into pathophysiology and causes and symptoms of endometriosis.
In endometriosis pain during menses or dysmenorrhea would be the most common presenting symptom and also the chronic pelvic pain. it may also present as severe congestive dysmenorrhea , pain during intercourse,cyclical bladder or bowel pain depending on the organ involved.
Uterus has an outlet for endometrium to shed but in abdomen the tissue or menstrual blood that fall down retrogradely has no outlet and start growing wherever it is fallen more common site being very, utero-sacral ligaments,peritoneum and fallopian tubes and in cup de sac..causing inflammation and pain , the severity of which depend on the extent and location of the implants.
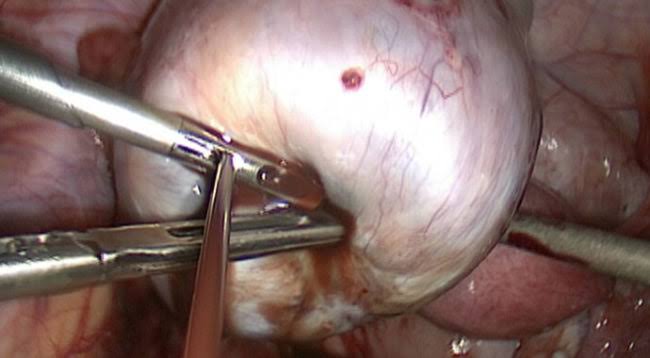
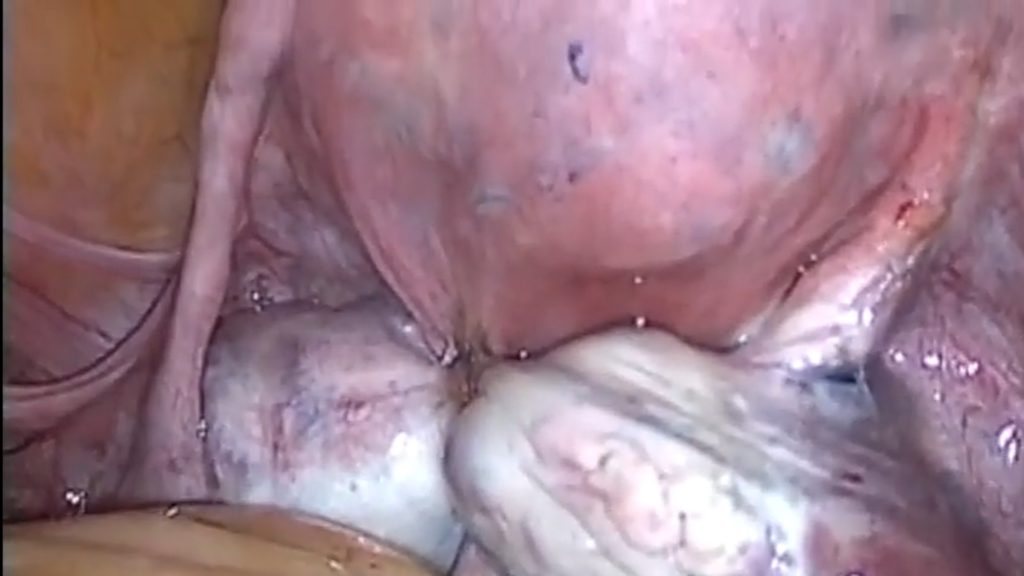
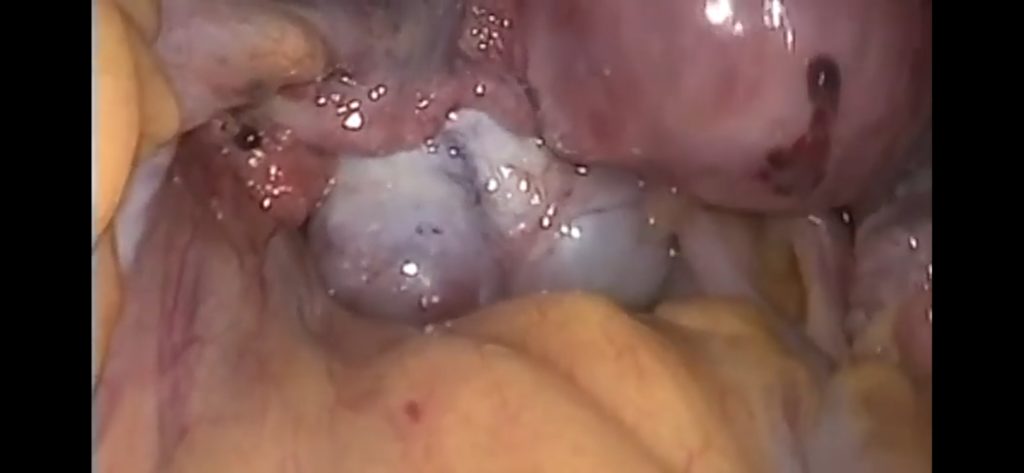
FOR management as complete eradication of disease is rare but can occur sponataniously or after pregnancy, the treatment of endometriosis therefore revolves around reducing and suppressing the disease or make the patient pain free. the choice of treatment depend on size,location and extent of disease and severity of pain. medical management options can either be hormonal or non hormonal medications.
sometimes surgical management is also required alongside the medical treatments and it be conservative when reproductive potential is preserved and radical when both uterus and ovaries are removed.
NON HORMONAL TREATMENTS:-
1.NSAID;- non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as the name suggest acts by suppressing the prostaglandin production which are the major mediators of inflammation. NSAID are used as first line of therapy to relieve pain and it does not interfere with the menstrual cycle.
2. Hot fomentation to lower abdomen and back can be used as a temporary relief measure.
3.physiotherapy and pelvic floor exercise can help to strengthen the the pelvic floor muscles and may increase endorphin recreation.
4. pain modifiers in the form of tricyclic antidepressants may act by modulating pain messages reaching brain from the site of origin.
5.TENS:- transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation uses electrode that send energy pulse into body that may block pain signals traveling to nervous system by production of feel good hormone or endorphins which are natural endogenous pain killers.
HORMONAL PREPARATIONS:-
1.OC PILLS.
2. PROGESTERONS.
3.ANDROGENS.
4.GONADOTROPHIN RELESING HORMONES.
5. AROMATASE INHIBITORS.
6.GNRH AGONISTS.
7.PROLACIN SECREATIN INHIBITORS.
8.MEFEPRISTONE.
9.LEVONORGESTERL RELEASING IUCD.
10.SELECTIVE PROGESTERON RECEPTOR MODULATORS.
As there is no role of medical management in grade 1 and 2 endo-metriotic disease then in such cases surgical excision became an option in the form of adhesiolysis of peritoneal adhesions,endometrioma excision,ablation of endometriotic implants,and oophorectomy in very severe cases.
As current understanding of disease is revolved around oestrogen suppression and its inhibition, treatment modalities needs to be individualised for each patients and more studies into molecular mechanisms and more research will be of help in improving the quality of life of patients suffering from this multifaceted disease..
