DR SACHIN V. NAIKNAWARE
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
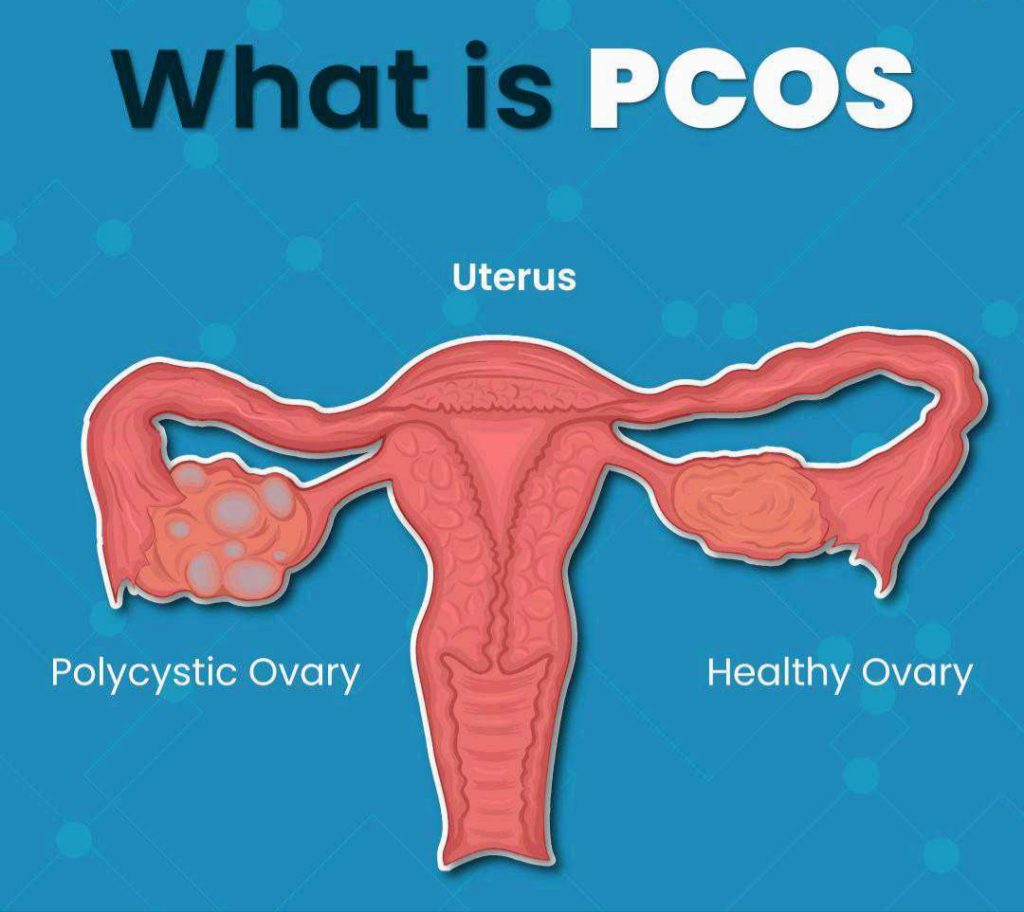
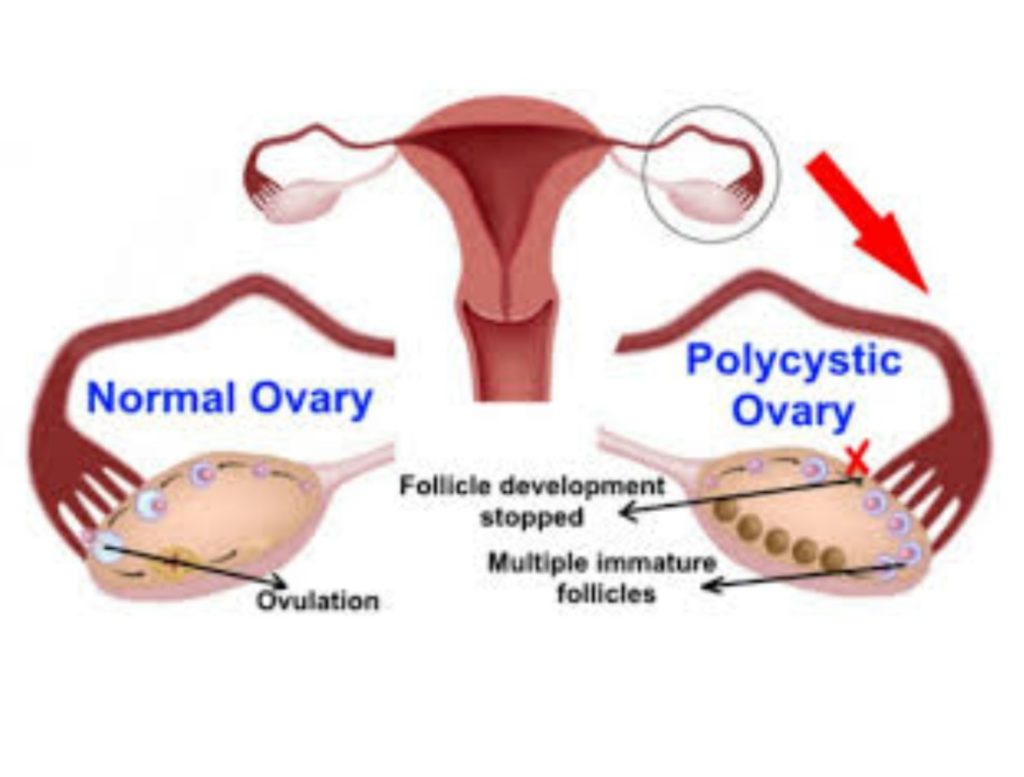
PCOD is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age group with prevalence of about 5-10%.clinically PCOD may present as ovulatory dysfunction in the form of oligo-menorrhoea, amenorrhea,hyperandrogegism and polycystic morphology on sonography.clinically this combination of symptoms were described by STEIN & LEVANTHAL in 1935.Approximataly 80% of cases anovulatory infertility are due to PCOD.
Rotterdam 2003 criteria entails following components for diagnosing PCOD as
- Oligo and or An-ovuation.
- clinical and biochemical signs of hyperandrogegism.
- polycystic ovaries on ultrasound.
OF THESE 2 OF THE 3 CRITERIA ARE NEEDED FOR DIAGNOSING PCOD.
Polycystic ovarian morphology is 12 Antral follicles (2-9 mm in diameter) in either ovary,an ovarian volume of > 10ml in one or both ovaries offers best specificity and sensitivity for diagnosing PCOD. exclusion of other causes of hyperandrogegism such as cushings syndrome,congenital adrenal hyperplasia,must be done by appropriate investigation.
Obesity,hyperandrogegism,and insulin resistance are factors that influence the symptom expression of PCOD. An-ovulation is most common in women with PCOD accounting for 80-90% of WHO Group II anovulatory infertility. According to AMERICAN SOCIETY OF REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE.the evaluation of infertility in women with PCOS should start after 6 months of regular unprotected sexual intercourse.
Treatment of infertility in PCOS patient include non pharmacological measures are weight reduction,lifestyle modification,pre conception counselling,and pharmacological agents with the mono follicular or bi-follicular growth and ovulation. Lifestyle modification with weight reduction of 5-10% of body weight reduction is associated with improved ovulation rate and hyperandrogegism correction.in addition to this body weight reduction is associated with reduced incidence of pregnancy complication and that during neonatal periods.
Women with PCOS have an increased risk of congenital anomalies in babies including but not limited to Heart and rural tube defects, Gestational DM, Pre-eclampsia, hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, and preterm birth, so preconception counselling and folic acid is of use in these patients.
Factors that contribute to sub fertility in PCOD are an-ovulation,metabolic and inflammatory factors, effects of obesity on oocyte quality and fatal development.Oocyte from PCOD patients shows reduced competence for development and reduced ability to complete meiosis and hyperandrogegism cause premature granulose cell leutinisation and impair cytoplasmic and nuclear maturation of oocytes. also intrafollicular microenvironment which is related to oocyte quality is affected by ovarian hyperandrogegism. Tessier et al showed higher intrafollicular testosterone level in patients with PCOD.
First line of treatment in patient with PCOS with an ovulation is Clomephine citrate for ovulation induction, this drug is oestrogen receptor modulator acting both as oestrogen agonist and antagonist.when administered in early follicular development ,it competes with oestrogen for its receptors in hypothalamus and pituitary blocking the negative feedback mechanism and increasing endogenous Gonadotrophin release cousin recruitment of follicles between 6th and 9th day of menstrual cycle.
Starting with the dose 50mg/day starting from day 2 to day 5 of cycle the dose may be increased upto 150mg/day depending on ovarian response.the ovulation rate achieved with can reach upto 75-80% with cumulative pregnancy rate of 60-70% and 22% conception rate per cycle. discrepancy in ovulation rate and pregnancy rate cana be explained by anti-oestrogenic effects of clomiphene on endometrium.
Advantages of clomiphene are low cost,oral administration and less monitoring needed.but clomiphene treatment should be limited to 6 cycles. about 15%of women with clomiphene does not ovulate and are termed as clomiphene resistant, in which cases gonadotrophin and surgical approach in the form of surgical ovarian drilling can be tried.in limited number of patients it can cause flushing,headaches,visual disturbances and abdominal discomfort and ovarian hyper-stimulation in 1-6% of patients.
As hyper-insulinemia is an well established feature in PCOS patients, use of insulin sensitising agents in the form of Metformin may improve ovulation rate in these patients . Metformin is an oral Byigusnide is commonly used,it causes reduced hepatic gluconeogenesis and increased peripheral glucose utilisation.it appears that Metformin is an advantageous reducing ovarian hyper-stimulation syndrome.
Second line of treatment in patients who are resistant to clomiphene is done with Gonadotrophines. before commencing treatment tubal potency needs to be assessed if not done earlier. starting with very low dose (37.5 to 75 IU/day) and increase according to response on serial measurement of follicular size . As gonadotrophin are costly rather than combining it with timed intercourse it needs to be used for ovulation induction with IUI. It is associated with ovulation rate of around 70% and clinical pregnancy rate of 20% in natural timed intercourse.
PCOD drilling is required is in some patients with PCOS. is considered as second line of treatment involving more cost and anaesthesia.
these punctures are done with monopoly cautery using cutting current for second and upto 4 punctures are made in each ovary.drilling acts by decreasing ovarian androgen secretion and consequently reduced peripheral aromatisation of androgen into oestrogen also it causes micro follicular environment more oestrogen facilitating follicular growth. An ovulation rate of 54-76% can be achieved with ovarian drilling patients in 6 months period after the procedure with pregnancy rate of about 28-56%. if there is no ovulation for 3 months after the drilling ovulation induction with clomiphene needs to be tried and if there are 6 anovulatory cycles after the ovarian drilling then gonadotrophin are used for ovulation induction.
IN VITRO FERTILISATION is 3rd line of treatment for patients with PCOS. IF PATIENTS ARE PRESENTED WITH BILATERAL TUBAL BLOCK,OLIGI-SPRMIA, count less than or equal to 5 million , IVF become the first line of treatment, along with lifestyle modification. in PCOD patients to avoid ovarian hyper stimulation suppression of endogenous LH by GNRH agonist allows follicular development. GNRH antagonist protocol for pituitary suppression hold promising in PCOS as they does not activate GnRH receptors and produce rapid suppression of gonadotrophin secretion in short span of time as in hours. and allows for short term treatments compared to long agonist protocols.
So to conclude women with PCOS undergoing IVF cycle respond differently as compared normal patients.so lifestyle modification , weight reduction, along with graded management from clomiphene to gonadotropins to IVF helps to improve the success rates. before closing the write up aromatase inhibitors are promising in casino mono follicular developments and reducing androgenic side effects associated with clomiphene and GnRH antagonist protocol appears to be safe allowing for GnRH agonist trigger and luteal phase support reducing the incidence of OHSS along with metfromin.
