DR SACHIN V. NAIKNAWARE. GYNAEC ENDOSCOPIC SURGEON.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Recurrent miscarriage as also known as recurrent pregnancy loss is defined as 3 or more consecutive clinically recognised pregnancy losses prior to 20 weeks of gestation.AMERICAN SOCIETY OF REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE has recognised RPL as 2 or more pregnancy losses. Approximately 15% of all clinically recognised pregnancies fail to develop.clinically recognised pregnancy is defined as pregnancy which is recognised on sonography or pregnancy tissue is seen in the histopathology report. In general 5% of all women will experience 2 or more consecutive miscarriages and 1% will experience 3 or more pregnancy losses. spontaneous pregnancy seems to be a common occurrence.
Sporadic isolated cases of pregnancy loss before 10 weeks of gestation can be attributed to chromosomal anomalies as Trisomy,Monosomy,or Polyploidy but the spontaneous occurrences of 2 or more pregnancy losses makes it a clinically distinct entity.As it is a psychologically and emotionally very disturbing for patients and their families. it is been observed that women with recurrent miscarriages tend to lose genetically normal pregnancies as compared to sporadic cases.Risk of sporadic miscarriages between 6weeks to 12 weeks of gestation is between 9-12% in women younger than 35 years of age and this risk is increased in women over 35 years of age due to increased incidence of trisomic pregnancies and in women more than 40 years miscarriage rate approaches 50%.
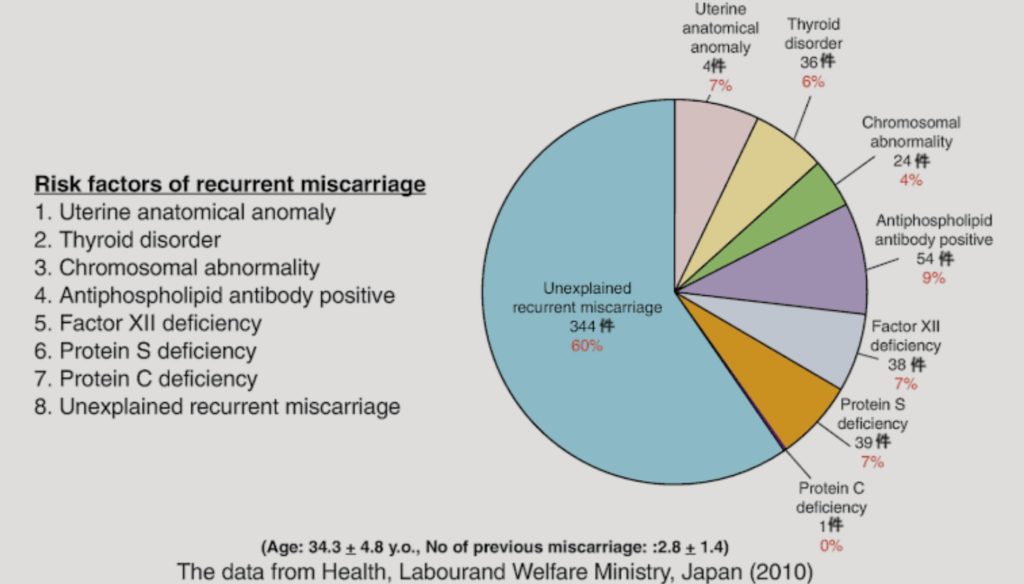
The recurrent miscarriages can occur and in approximately 50% of cases no cause can be found. following are the causes most commonly found in patients of recurrent miscarriages.
- GENETIC FACTORS (2-5%)
- ANATOMIC FACTORS(10-15%)
- ENDOCRINE FACTORS.(17-20%)
- AUTOIMMUNE.(20%)
- INFECTIONS.
- THROMBOTIC CAUSES,NON APS,THROMBOPHILIAS.
- ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS.
- UNEXPLAINED CAUSES.
For prognostic purposes RPL can be defined as primary or secondary. in primary RPL women has no prior successful pregnancy. in secondary RPL pregnancy losses occurs following successful live births.
RPL due to parental chromosomal defect involves reciprocal or Robertsonian translocation in 2-4% of patients.in some small genetic studies it has been observed that in 36-39% of couples RPL is associated with Unbalanced structural chromosomal rearrangements. Karyotyping and genetic counselling is an important aspect of management as likelihood of future healthy pregnancy depend on chromosomes involved and type of rearrangements.
Anatomic abnormalities can cause RPL in 10-15% of patients by disrupting blood supply to endometrium or by causing poor placentation . commonly detected abnormalities are unicornuate uterus, bicornuate uterus,septet, didelphid or arcuate uterus but uterine septum is most commonly found, and correction of septum hysteroscopically has much beneficial effect.
Surgical management of any sub mucous fibroid and intramural fibroids more than 5cm in size has also beneficial effect.uterine anomalies can be diagnosed by clinical examination, ultrasonography, 3-D OR 4-D scan and if needed by MRI SCAN. hystero-scopy has the advantage of diagnosing and simultaneously treating the condition in same sitting.
Endocrine disorders are found in 17-20% of couples with RPL. it includes Thyroid diseases,PCOD, Luteal phase defects, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, .LPD is a term used to describe decrease in amount or duration of progesterone secretion from corpus luteum or lack of response to ovarian steroids. LPD is diagnosed by morphological examination of timed luteal phase endometrium sample according to NOYE”s criteria.as persistent lag of more than 2 days in histologic development of endometrium compared with menstrual cycle days.
Nearly 40% of patients with RPL shows some evidence of PCOS as evident by elevation of LH & ANDROGEN & INSULIN persistently causing hyperi-nsulinemia as seen in TYPE 2 DM. poorly controlled TYPE 1 DM is more casual factor in RPL. hyperinsulenimia causes RPL by altering HPO AXIS. Anti-phopholipid antibody syndrome constitute an important cause of RPL.is found in 5-20% of patients. these antibodies are diverse and variable from patient to patient.
Psychological factors are also implicated in the ethology of RPL, along with some lifestyle factors as cigarette smoking more commonly is associated with RPL due to nicotine content which has vasoconstrictive effect, also positive link is found between alcohol consumption and caffein consumption.
Inspite of large scale studies and research into the subject no apparent cause can be found in about 50% of cases of RPL. the treatment recommendations should be based on underlying cause of RPL. most effective therapy for RPL due to unexplained causes is antenatal counselling and psychological support,making them feel positive and emphasising about chances of successful future pregnancy as evidenced by studies is high and can exceed 50-60% depending on maternal age, parity and so to conclude correction of endocrine disorder, antip-hopolipid syndrome,and surgical correction of uterine anomalies has highest successful pregnancy rates and in the cases of unexplained RPL progesterone has shown to be effective and beneficial in decreasing miscarriage rate in women who had RPL. karyotype analysis of products of conception is useful in the setting of ongoing treatment of recurrent pregnancy losses.
